The industrial robotic arm’s influence in the production industry is spreading due to their efficiency, higher productivity, and cost savings. Many businesses with robotic arms can save on costs essentially in low-skilled human labor with reduced human error and waste. In addition, the robotic arms can increase productivity and efficiency with more extended operating periods of the same strength, accuracy, and repetitive, programmed actions.
So what are robotic arms? Robotic arms are mechanical arms that are generally programmable, having similar functions to a human arm. This machine can be a mechanism on its own or be part of a complex robot. Let’s discuss further the uses, benefits, and types of industrial robotic arms.
Knowing the Industrial Robot Arms
In keeping with the IFR (International Federation of Robotics), robotic arm is a robotic system designed for production that is programmable and automated to perform physical, production-related tasks without a human controller. This consists of three or more axles, making them capable of movement.
The general applications of an industrial robotic arm are welding, painting, assembly, pick and place, packaging, labeling, palletizing, product inspection, and testing. In addition, it can assist in material handling and administer interfaces. The robotic arm accomplishes its tasks with speed, high endurance, and precision. As a result, it is commonly found in the production industry.
The Essence of Robotic Arms
There are a few reasons why robotic arms are being used in production facilities. First, industrial robotic arms are capable of mimicking human motion. With the ability to mimic human action, they are used and placed in areas that:
- need to reduce dangers towards humans,
- need more strength or accuracy than humans,
- a continuous operation is required,
- or roles assumed to be too dull to human workers.
Secondly, many robots can repeat actions and motions with precision while being operable 24 hours a day. This makes them a highly desired commodity in the production field.
Lastly, the accuracy of robot arms is reliant on the correct calibration and maintenance of the machine. One example of an industry that depends on robotic arms is the light industry. The lighting sector has special interests in robotic arms due to SMT’s (surface mount technology) and polar’s pick and place, spot welding, and arc welding functions.
Different Types of Robotic Arms
Many different robotic arm types are available on today’s market. Each is designed with essential core abilities and functions that make each type particularly well-suited for distinct industrial environments. This section will explore some of the commonly deployed types of programmable robot arms used in the production sector.
Here are the four widely used robotic arms:
-
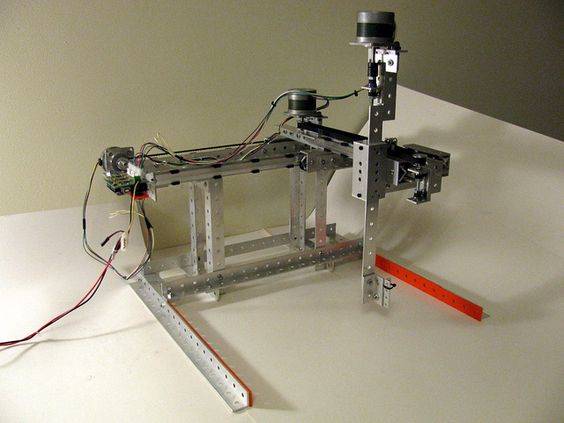
Cartesian Robotic Arms
 Source: Pinterest
Source: Pinterest
Cartesian robot arms, named after the Cartesian coordinate system, are often known as rectilinear or gantry robot arms. The Cartesian coordinate system was developed by René Descartes in the 17th century to map geometric curves onto a graph using algebraic equations.
In robotic arm terms, mechatronic Cartesian robots consist of three programmed articulating joints, using the X, Y, and Z coordinates. This is to specify linear movement in three dimensions along these three axes. In addition, the wrist joint often provides other rotational functionality.
Cartesian robot arms can be mounted vertically, horizontally, or overhead. Also, they are commonly used in machining parts or picking and placement along with conveyor belts.
-
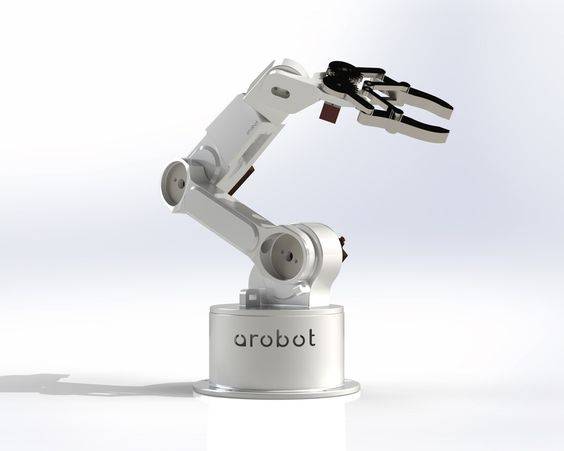
Cylindrical Robotic Arms
 Source: Pinterest
Source: Pinterest
In contrast to the Cartesian versions outlined above, cylindrical robot arms are ones whose axes form a cylindrical coordinate system. Essentially, their programmed movements occur within a cylinder-shaped space (up, down, and around).
These robot arms are commonly used for spot-welding, assembly operations, and machine tool handling, where robotic arm components, like rotary and prismatic joints, showcase a linear and rotational motion.
-
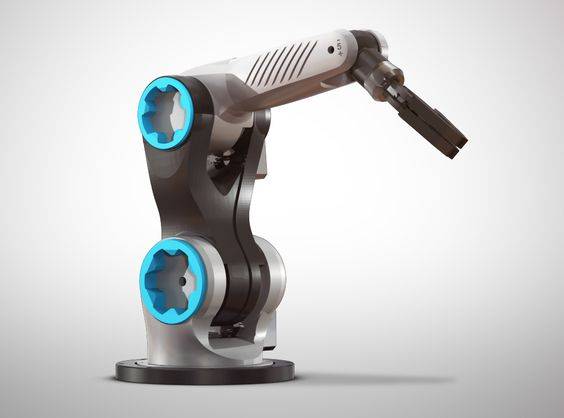
Spherical Robotic Arms
 Source: Pinterest
Source: Pinterest
Similar to the cylindrical robotic arms, a spherical or polar robot arm functions within a spherical work envelope or potential locus of movement. This is carried out through a combined rotational joint, two rotary joints, and a linear joint.
The polar robotic arm is connected to its base through a twisting joint. The subsequent spherical workspace can perform similar roles as cylindrical robotic arms, such as handling machine tools, die casting, spot welding, and arc welding.
-
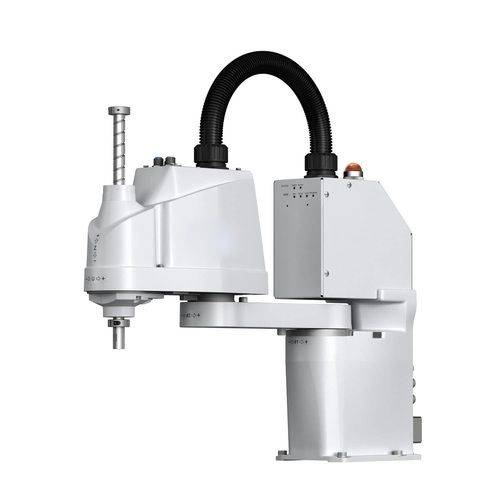
SCARA Robotic Arms
 Source: Pinterest
Source: Pinterest
SCARA robotic arms are the most widely used assembly and pick-and-place applications. The acronym SCARA stands for Selective Compliance Articulated Robot Arm or Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm. This refers to their flexibility along some axes and ability to tolerate a limited degree of compliance while remaining rigid in others.
SCARA robotic arms are considered classic when thinking of a high-tech production line. Their certain compliance features make them ideal for these purposes. So for placement tasks and specific assembly, using these tools is highly advantageous. Moreover, they will not bind or damage any parts, even if you need to insert additional details into tight-fitting spaces.
Conclusion
In a nutshell, industrial robotic arms are positively impacting the manufacturing industry. The benefits are still growing with newer robotics coming out with unique specs. What’s exciting is that we could be looking at a future where robotic arms labor is the norm in every production facility.
What are your thoughts about the article? Please place your comments in the box below.






Add Comment