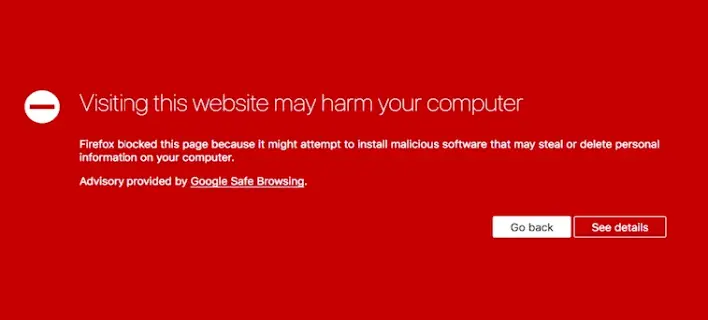
We all know that visiting the wrong website or downloading the wrong file can have catastrophic effects on your computer. But how likely are you to run into a malicious website today? Especially considering how many cybersecurity businesses are actively combating the problem. The answer – a lot, and the battle keeps raging on.
What Is a Malicious Website?
When most people think of malicious code, they think of a piece of software that is downloaded to the victim’s computer, sometimes unwittingly. However, there are a number of ways in which a website can infect a visitor’s computer. This is especially true if the visitor has an outdated web browser or is missing important security steps to take.
Similarly, many malicious websites masquerade as legitimate websites, especially websites that users would expect to download an executable file from. Users will connect to these websites and willingly download and run the malicious software because it has the appearance of being the legitimate software that they were looking for. This is a more effective way of distributing malicious software because it can potentially undercut measures the user might take to protect themselves.
How Prevalent Are Malicious Websites?
The internet is a very big place and there’s a lot going on out there. Around one in every 100 websites on the internet are infected with malware at any given time. Meanwhile, the average website is subject to 44 malicious attacks every day on average, attacks that are often undertaken by bots probing for vulnerable websites.
Websites that are vulnerable to attack can experience unauthorized access to their systems, vandalism of their homepage, or the installation of malicious code. This enables attackers to turn legitimate websites into unwilling accomplices to their activities.
The average rate at which websites are attacked has been on the rise, according to Sitelock’s Website Security Insider report, which analyzed common malware and malicious websites on the basis of reports from around six million users.
The analysis showed that the number of their customers’ whose websites were infected increased by 20% during the last quarter of 2018, in comparison to the same quarter last year. Between Q3 and Q4 of 2018, Sitelock noted an increase in the percentage of infected websites, going from 0.8% of the user base to just over 1%. As Sitelock pointed out, this represents an additional 18.5 million websites being infected.
Most of Sitelock’s customers are small businesses and blogs – exactly the kind of websites that attackers like to target. These types of websites generally have less sophisticated prevention and detection methods than big websites and businesses. This increases the chances of an attacker being able to plant malicious code on the website and leave it there unnoticed for as long as possible.
Combating Malicious Websites
In order to effectively combat the impact that malicious websites can have on unsuspecting internet users, we need both websites and internet users themselves to better understand the risk. One of the more surprising cybersecurity issues is how vulnerable the average website is to an attack. Security experts suggest that the average website contains hundreds of pages that are vulnerable to SQL injections and XSS attacks – two of the most basic attack vectors out there.
The first and most important thing that any of us can do to enhance our online security is to make sure that we keep all of our operating systems and applications fully updated. This is important for both users and website owners. In some ways, computer viruses do act like viruses in the real world. One similarity is that it is possible for a system to carry a virus without showing any symptoms.
Fortunately, there are cybersecurity organizations out there who are helping us to combat the scourge of malicious websites. This includes businesses like Norton, Kaspersky (sometimes), and other antivirus developers, as well as individuals like the legendary security researcher Mikko Hyppönen.
Sitelock, whose report we cited earlier, provides websites with automatic protection from common threats, such as DDoS attacks, where an attacker tries to bring a site down by initiating a large number of simultaneous connections. These attacks are designed to overwhelm servers, but they can be defended against.
Beware the Unknown
Never click on any link that you don’t recognize or aren’t expecting. Even if the link looks like it is being sent from an email address or social media account that you recognize, verify with the person sending it that it is legitimate first.
This also applies to email attachments. It is very easy to embed malicious code in a media file or document. When these files are opened, the malicious code is executed. Hence, this type of malware is known as a Trojan, after the horse, of course. Those downloads we mentioned earlier that masquerade as legitimate software are also examples of trojans.
Held to Ransom
Ransomware attacks have been increasing in prevalence and have caused alarm among many in the cybersecurity industry. Ransomware attacks have led to businesses paying huge ransoms to criminals. This type of attack uses malicious code to encrypt all the files on a network. The key to decrypt the files is only released after a substantial payment has been made to the attackers.
This type of attack is so successful, not only because once they take hold they are difficult to dislodge but because criminals know that they can demand a significant ransom from a business and still come in way under the cost to the business of losing all their data. As a result, it is a very effective form of blackmail.
The mere existence of ransomware should deter anyone from downloading unknown files onto their work computers. In fact, unless there is a work-related reason for downloading something, keep it off any machine that you use on your corporate network. You don’t want to be the person responsible for your employer’s data being held to ransom. If you use your business laptop as a personal computer, you need to be extra careful.
The reality is that there will always be malicious websites and malicious actors looking to exploit legit ones. Fortunately, there are organizations out there dedicated to making the internet as safe as possible. We can all do our bit to help this effort by helping ourselves and learning some basic cybersecurity tips.






Hi Atish Ranjan
The Battle Against Malicious Websites is very helpful article…. the same thing happened with my computer… thanks for sharing this information… thanks a lot….
That’s why I always visit those sites which have SSL certificates enabled and in a new tab of my browser. Thanks, admin for this great post.
Hi Atish,
Once I have accidentally downloaded a software from a malicious website which automatically triggered ads on my system. Thanks for this guide to prevent such websites.
Hello Atish,
Great Post. In this digital world, Spoofing and hacking attempts are normal. If you are not aware of what type of website we are browsing can harm your computer. If we open a malicious website than it might inserted viruses and spyware through browser to our computer. You have shared some great tips here.
Regards,
Vishwajeet Kumar
Thanks for this article. I did land on an “malecious website” earlier, closed it before it harmed my computer. So sneaky!
This is a desperate battle. We have to face so many malicious websites all the time ! So many people are victims of hackers. Anyway, thanks for our insight.