You might have come across the terms like RAID and RAID controllers while going through the specifications of Dell PowerEdge Servers. Understanding these two terms is very important, a raid controller can support different types of hard drives. RAID can be abbreviated as a redundant array of independent tasks.
With RAID controllers, you will be able to save the same data in different locations on multiple hard drives, and it helps to preserve data during hardware failures. The duty of RAID card is to manage hard drives of a personal computer and ensure that all the drives work jointly to deliver super-fast performance.
In earlier days even small-sized RAID cards used to be very costly, but nowadays they became very cheaper. Coming to the main use of Raid disk subsystem, it boosts up I/O performance. The group of physical disks will resemble like a solo storage unit for the host system; sometimes it also appears like multiple logical units.
Multiple drives can be accessed easily resulting in an improvement in the data throughout. If data loss is occurred due to a physical disk failure, then the lost data can be brought back by restoring the other physical disk where data is being stored. Don’t mistake a RAID type to be a good data backup source and it will not offer enough security for your data. Understanding the RAID levels
There are various types of RAID levels; you don’t need to worry if you are unaware of them as we have clearly mentioned about each RAID type in this post.
Some featured concepts of RAID
You will come across some features like Striping, Mirroring, and parity method when you go through different types of RAID levels. Check the
Parity Method
The data that is lost from one drive can be restored from the parity’s stored data by using the parity method. Some of the variants that make use of this parity concept are RAID 5 and 6.
Striping in RAID types
It is nothing but distributing the data randomly across multiple disks so that the lost data can be retrieved in case of disk failures. When disks are striped, the data is not completely saved into a single disk. Suppose if you use four disks, 1/4th of the data will be equally shared with all disks.
Mirroring
If you look in a mirror, it shows the replica of your face. In the same way, there is a term called mirroring in RAID. It is the process of making a replica of identical data in different disks. The content of one will be copied to all other disks too.
What is RAID 0?
RAID 0 is the first the one among all the RAID levels that utilizes disk stripping to ensure high data passage in a system where there is no need for data redundancy. Every physical storage space that is available in the system is divided or partitioned into sixty-four stripes sequentially arranged one after the other. The disadvantage of RAID 0 is that it won’t guarantee the data redundancy and its capacity is very limited.
Additional storage and enhanced performance are the advantages of RAID 0. One more reason why people won’t prefer RAID 0 is that if any disks fail to function, it would result in complete data loss. It would be very difficult to run applications that deal with editing photos and videos.
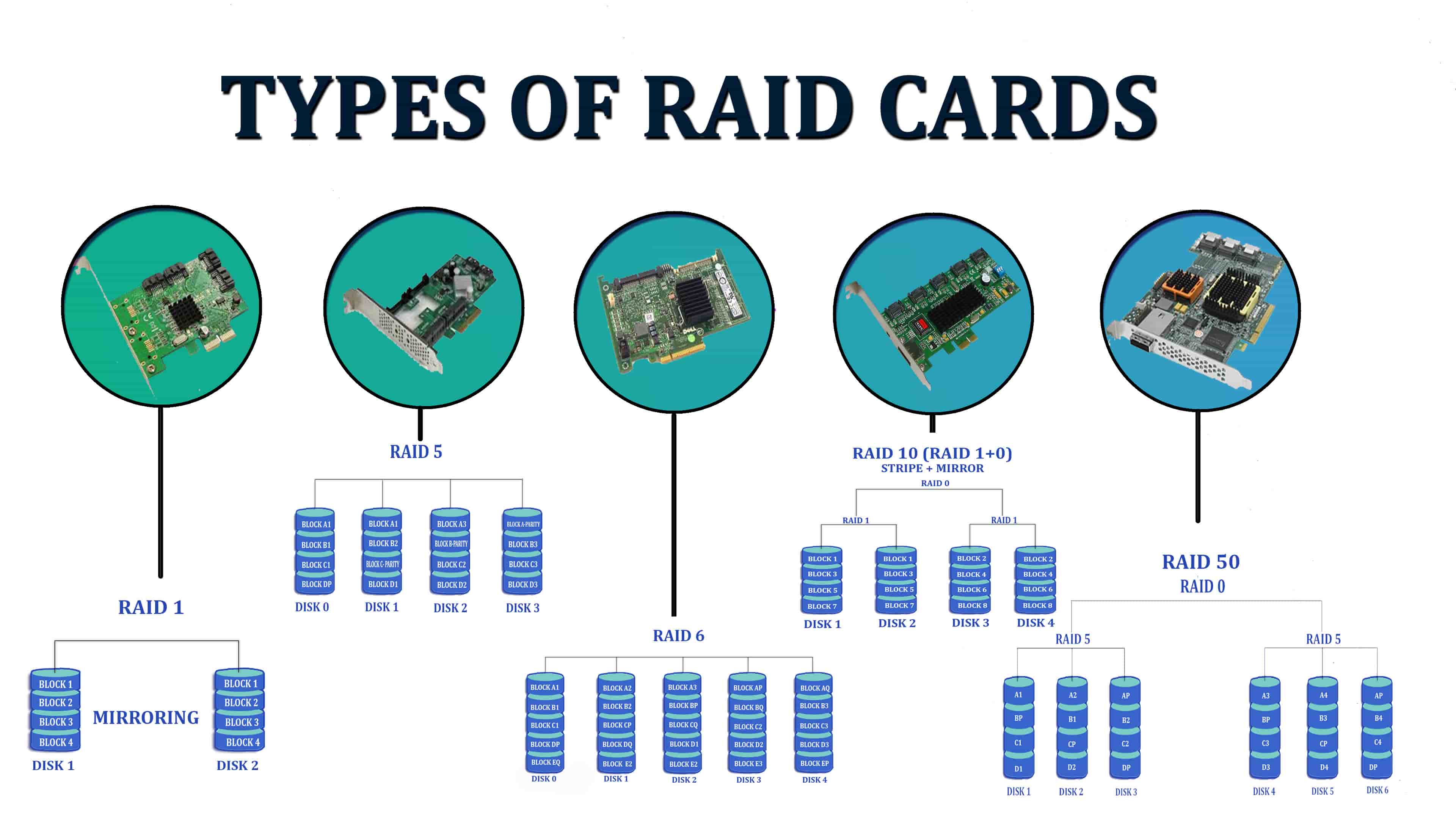
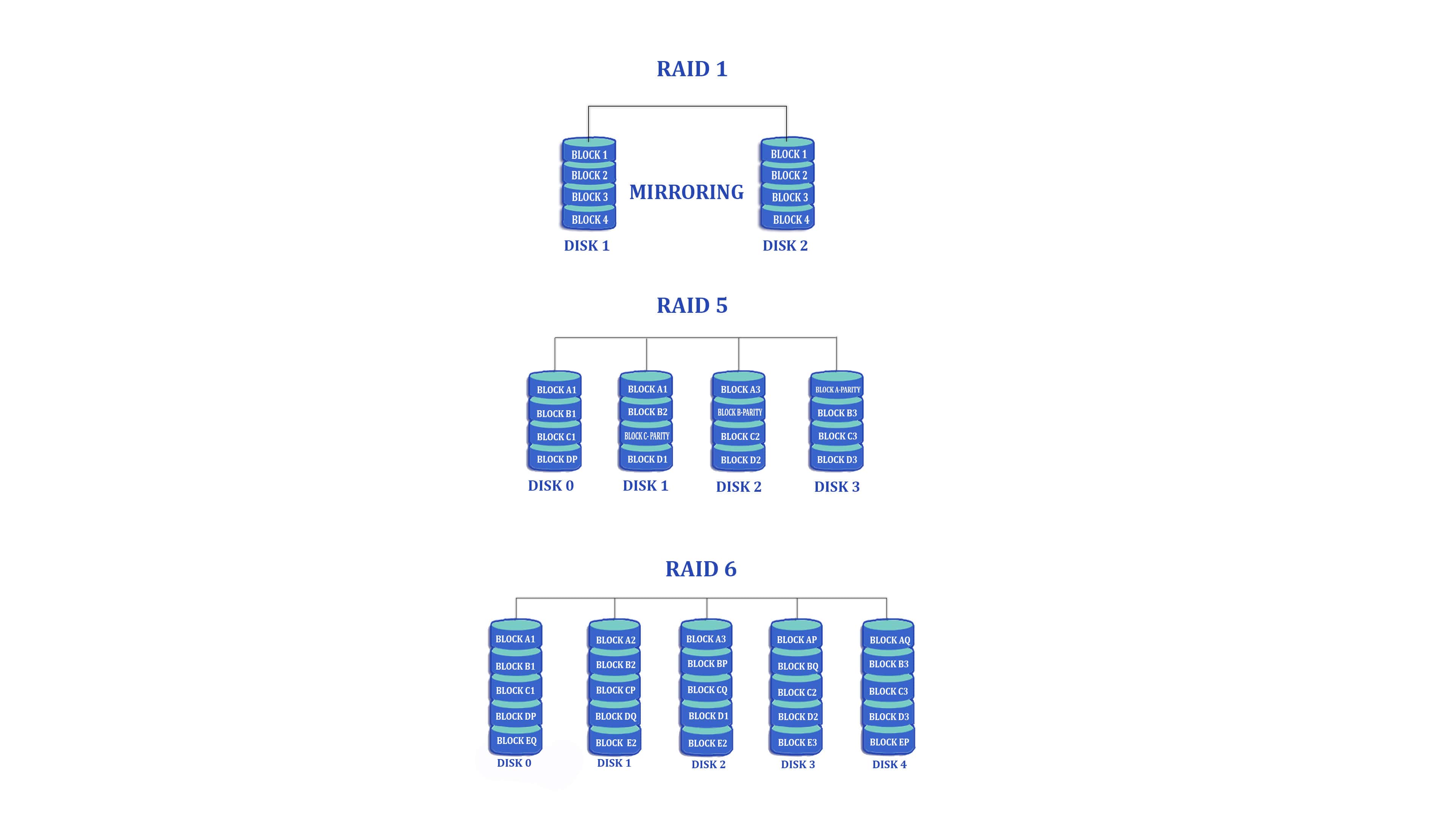
RAID 1
It is the second variant that makes use of disk mirroring. The main advantage of RAID 1 is that the data that is written on one disk will be immediately copied to the other physical disks. If any disk fails to function, then it makes use of other disks to operate the system and reconstruct the unsuccessful physical disk.
RAID 1 helps to obtain 100% data redundancy which is one of its main advantages. As the data of one disk is copied or written on the second one, your system won’t get affected even with the failure of the first disk.
RAID 5
It offers data throughput for small conscious access. RAID 5 even uses disk striping to give huge data throughput. The controller of the system uses parity data to restore the lost data during the drive failures. Parity data will be equally distributed among all other disk spaces in the system.
By using RAID 5, you can run as many numbers of apps of that you want until and unless high capacity SATA drives are not used in your system. As parity data is dispersed equally to each and every drive of the system, the overall read performance would be very less when compared to other RAID types.
RAID 6
RAID 6 is just similar to Raid 5, but few features are extended in this one. One extra parity block is used in RAID 6. It safeguards your system against dual disk failures and misfiring that do occur during the rebuilding process of a single disk.
Disk striping and dual distributed parity are combined together in RAID 5. Parity renders redundancy for the failure of a single disk without making a carbon copy of the contents of all the physical disks available in the system. Drive capacity can be efficiently used with RAID 6 server. If you are using a system that has SATA drives with huge capacity, then you should go for RAID 6. It will be very useful for programs that can take the edge of performance on time.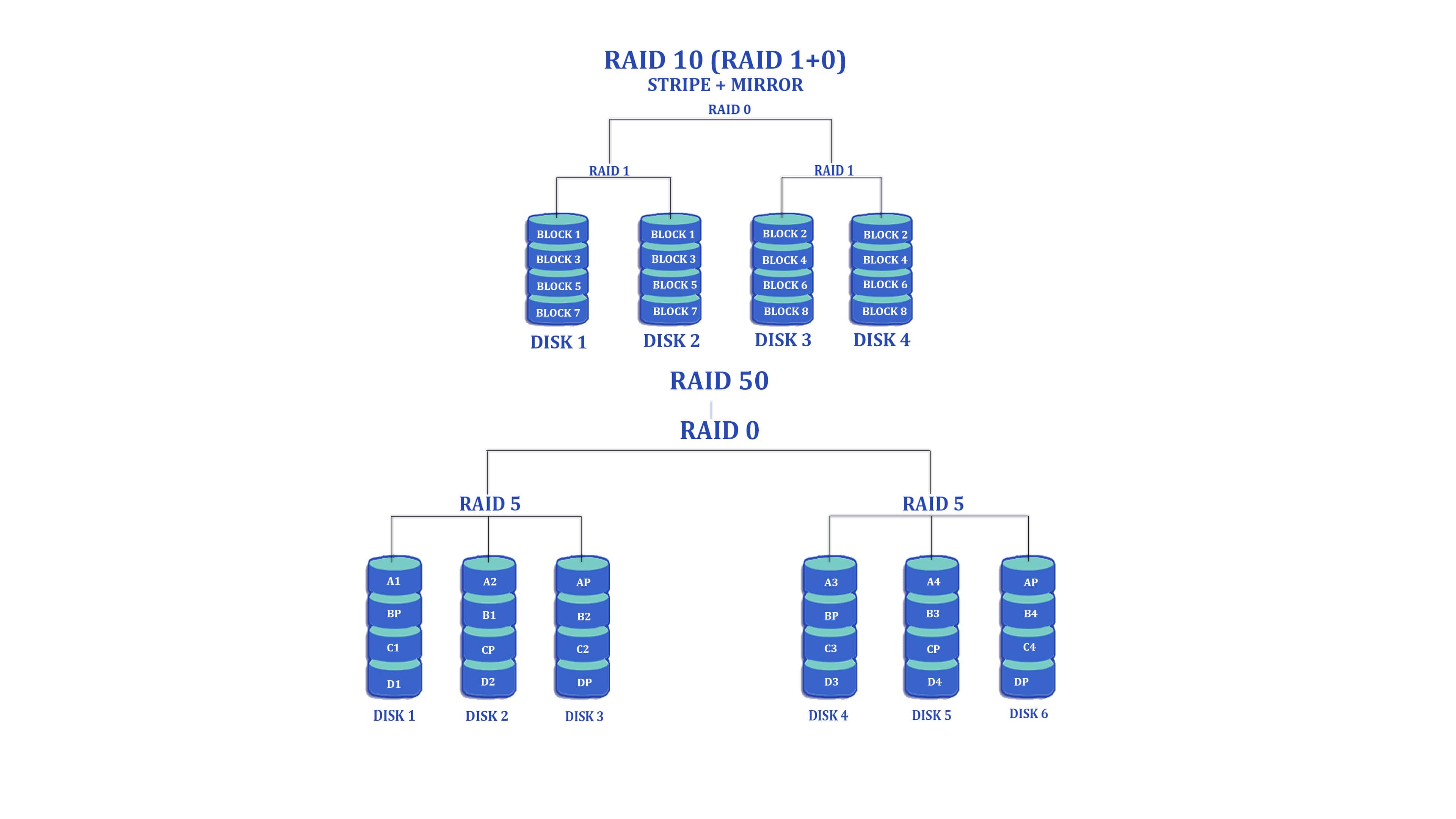
RAID 10
It is a combination of two RAIDs, i.e. 1&0 and the disk striping will be done over mirrored disks. In order to efficiently operate RAID 10, it needs either two or more than two mirrored sets running together. Two or more RAID 1 sets are mixed together to shape up a single array. In RAID 10, data will be striped wholly over the mirrored drives.
In RAID 10, there are two variants, i.e. RAID 0+1 and RAID 1+0. If you are handling the applications that need high performance than RAID 0, then it is good to choose RAID 10. It suits best if you are running applications that deal with transactional databases. Coming to the disadvantages, RAID 10 is a bit costly when compared to all other types.
No drive is left without being mirrored in RAID 10, and there won’t be any delay in the system because party calculation will not be done. The benefit of this RAID strategy is that it can bear and overcome the loss of two or more drives unless and until the two drives of same mirror pair fail to work. The disadvantage of RAID 10 is that it is highly expensive when compared to all other raid cards.
RAID 50
RAID 5 and RAID 0 are blended together to form RAID 50 that need a maximum of six disks to work well. The increased advantage is the major benefit of RAID 50, and when you look at the drawbacks, the cost associated with this type is very high, and its usable capacity is very low.
RAID 50 comes with two different variations, i.e., RAID 0+5 and RAID 5+0. Coming to the first variant, it uses more than two RAID 5 sets. They are linked together in a one RAID group that increases the reliability of RAID group. The increased reliability helps the system to bear and overcome the disk faults and failure in any one or both of the RAID 5 types. RAID 5+0 is the form of RAID 50. This will be very useful in situations where there is a need for better performance and where RAID 5 economics are very important.
When you purchase any system or a server, it comes equipped with a RAID card that you have chosen while placing the order. You don’t need to put your efforts to install RAID as it comes configured and it will be in working condition. If you plan to change the RAID card after receiving it, then there are many ways with which you can modify the level of RAID card with the help of a software. It is even possible to change RAID level without losing the data by using the controller interface. The hardware or software controller that manages the RAID is not generally visible to the end user.
Conclusion
While choosing the RAID type, you should be very careful and analyze all your work requirements well in advance. Your decision must depend upon your input and the output operations. You should also consider the data security while selecting the RAID variant for your server. It helps to improve the server performance and quickly recover from the failure of hardware components. RAID is not for data back up, and it would be good to deploy a separate storage system for data backup and recovery. Even after the rise of SSDs that come with no moving parts, RAID still remains a firmly fixed part of the data storage now.






Really amazing post I enjoyed very much.Thanks for sharing this great content.Keep up the good work
Hi Shelly,
Very informative post, honestly I didn’t have any idea about RAID Controllers!
Thanks for sharing!